There are thousands of algae species. In the classical classification of algae, the Chloromonadophyta, yellow-green algae, gold algae, diatoms and the brown algae are counted as classes to the group Heterokontophyta.
Green algae
Green algae types such as Chlorophyta, Chlamydomonas, Spirogyra, Cladophora, Hydrodictyon, Volvox, Spirogyra – spiral algae, Plantosphaeria, Sphaerocystis. The green algae also include the filamentous algae, which form green algae wadding. They often appear gelatinous.
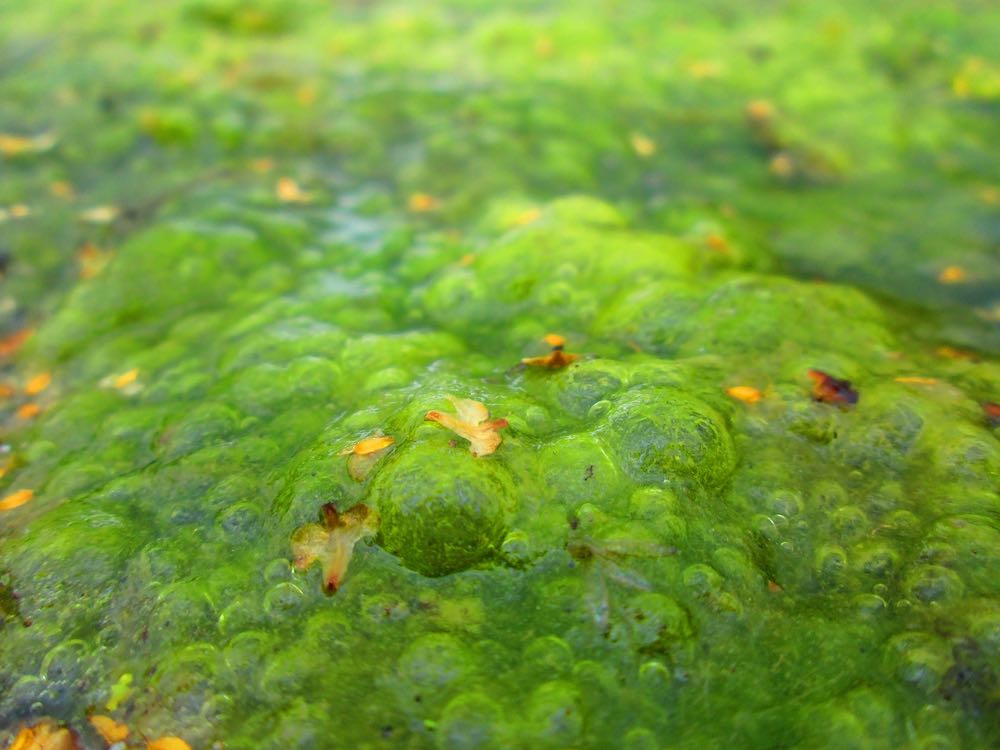

Blue-green algae
Blue algae (cyanobacteria) are not algae, strictly speaking, but bacteria, which at first glance have a similar appearance to algae and are commonly counted among them. With strong eutrophication, ie too high nutrient content, massive surface blooms or algal blooms form.
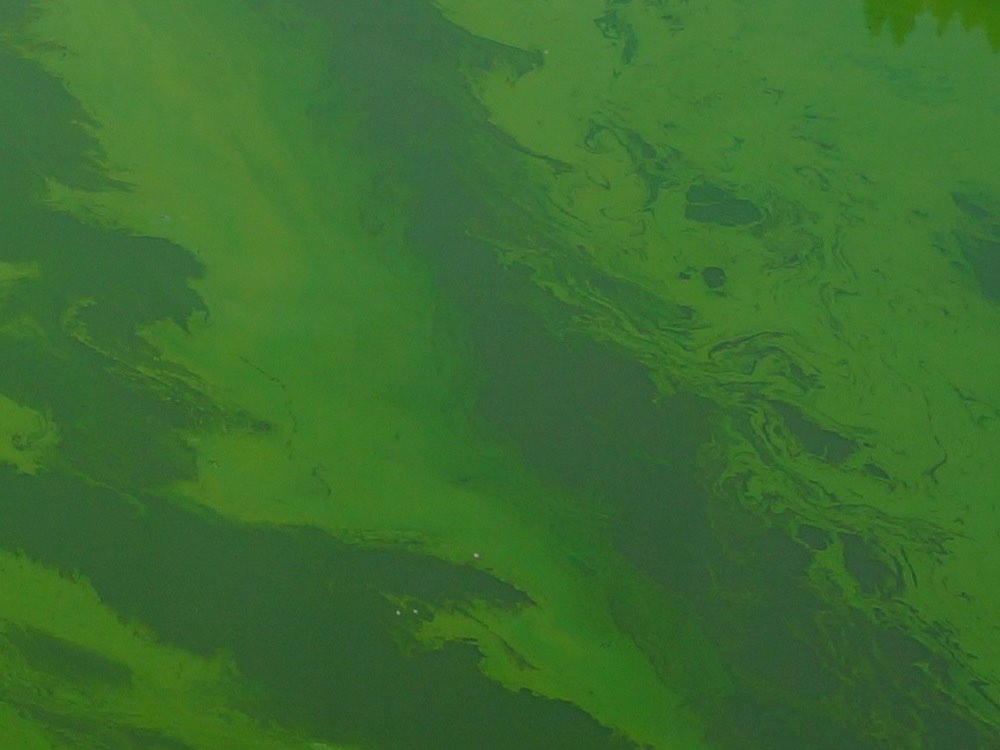

Brown algae
Brown algae (Phaeophyceae) look brownish and have a form of branched filaments in the garden pond. Brown algae are often found on plants and stones in fresh water
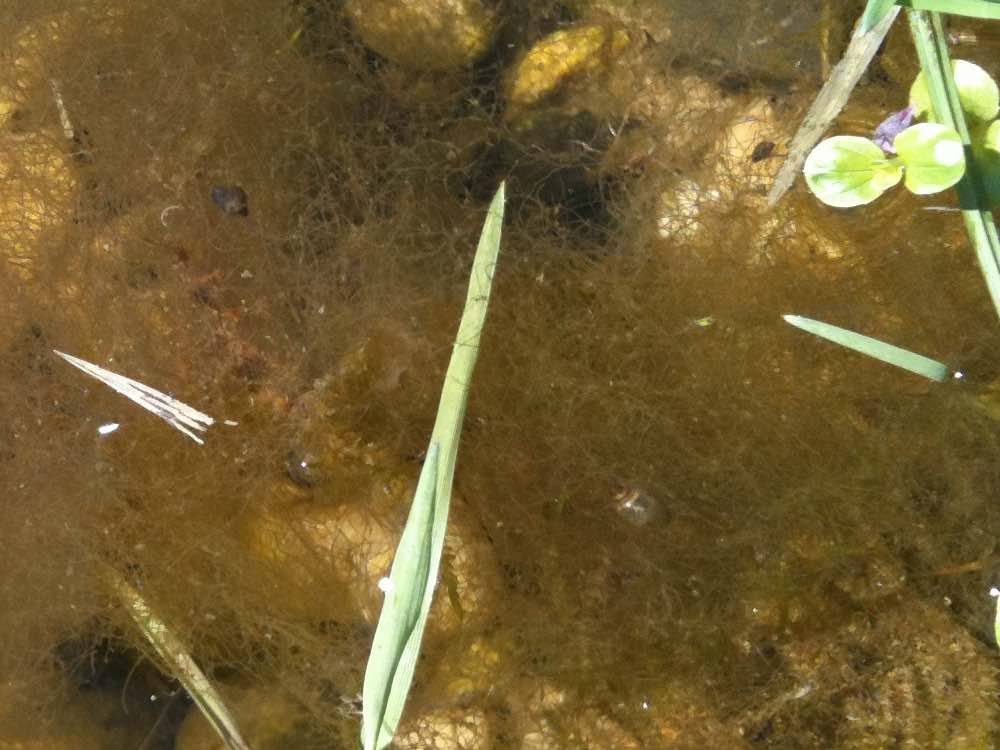

Brown algae in the saltwater look completely different, with large leaves and form up to 100m long threads, with which they root themselves in the soil. Brown algae in the sea can be found in cooler regions.
Diatoms
Diatoms (Bacillariophyta) are brown colored and called by a hard mineral shell, a cell envelope also Frustel. The brown alga consists mostly of silicon dioxide, as well as the brown alga. Silicon dioxide (SiO2) has the property of being very hard and is resistant to chemical agents.
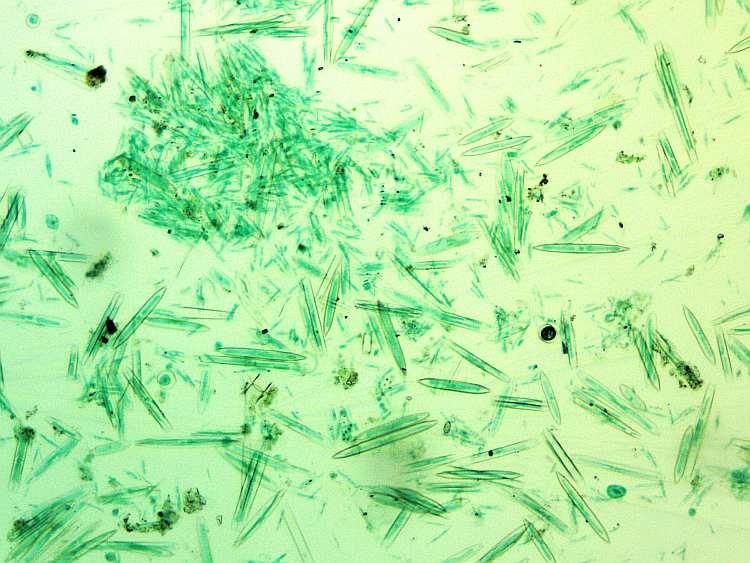
More information about various types of algae:
- Chlorella & spirulina algae as a nutritional supplement for humans
- Yellow-green algae (Xantophyta): only live in fresh water
- Golden algae (Chrysophyceae): rarely marine, mostly found in fresh water
- Red algae (Rhodophyta): predominantly in the littoral zone of the sea or saltwater aquariums
- Green algae (Chlorophyta): Sea, freshwater and also algae, filamentous algae
Spirogyra algae cell under the microscope
These photos were taken with normal optical microscopy techniques under 400 magnification and show the effect of clicks on the algae cells:

Healthy spirogyra in front 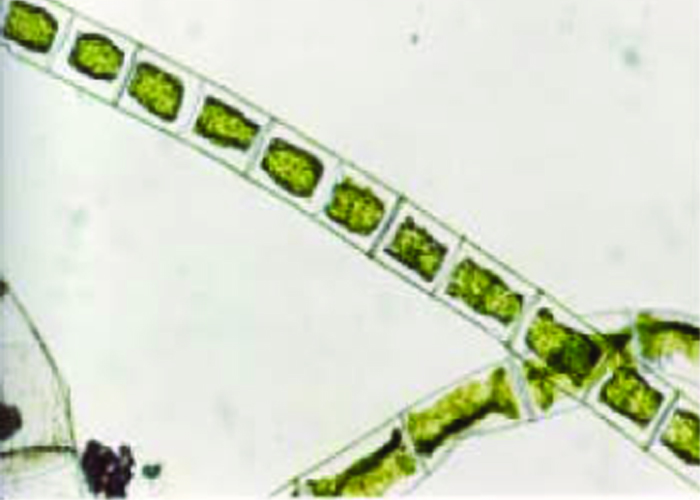
Spirogyra after 14 days: the cell structure of the cells are badly damaged 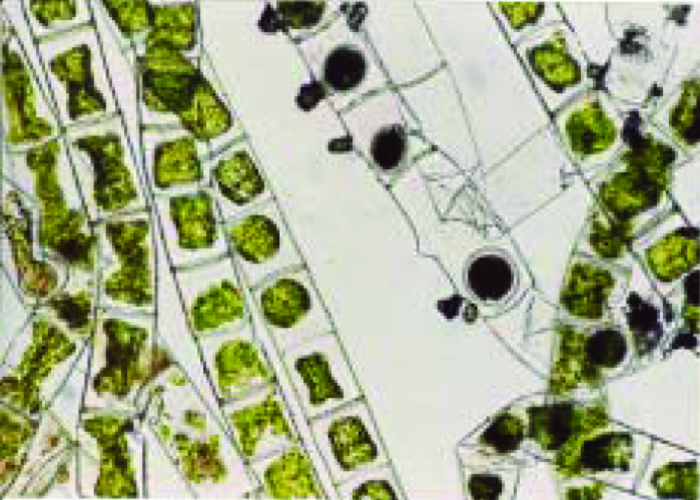
Spirogyra after 21 days: many cells are dead
The algae release creates acoustic clicks and emits click sounds under water. The hollow bodies, vacuole of the alga get into a squeeze through the high-precision clicks and tear. The cell juice comes out and the alga dies naturally.
Other species of algae under the microscope
Image source & friendly permission by NERC CEH
Fragilaria Crotonensis 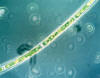
Mougeota 
Navicula 
Oedogonium 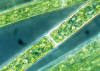
Rhizoclonium 
Spirogyra 
Tribonema 
Zygnema 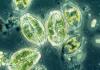
Amphora 
Anabaena 
Cladophora 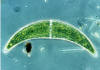
Closterium 
Coleochaete 
Cosmarium 
Cymbella


